Dealing with family law issues can be stressful, especially when safety is a concern. If someone is facing threats, harassment, or violence, a temporary order of protection (TOP) can provide immediate legal protection. But what is a temporary order of protection, and how does it work?
In this guide, we’ll break it down in simple terms. Whether you need one for yourself or are dealing with one issued against you, understanding the process can help you take the right steps.
What Is a Temporary Order of Protection?
A temporary order of protection is a court-issued legal document that restricts the actions of one person (the respondent) to protect another person (the petitioner) from harm. These orders are commonly used in situations involving:
- Domestic violence
- Family disputes
- Harassment or stalking
- Criminal cases involving assault or threats
A temporary order of protection is exactly what its name suggests—temporary. It is designed to provide immediate legal protection until a judge can hold a full hearing to decide whether a longer-term order is necessary.
How Does a Temporary Order of Protection Work?
A temporary order of protection can be issued quickly, sometimes on the same day a request is filed. Here’s how the process typically works:
1. Filing a Petition
The person seeking protection (the petitioner) must file a request for a temporary order of protection in Family Court or Criminal Court. They will need to provide specific details about why they need protection, including any history of violence, harassment, or threats.
2. Judge’s Review
A judge will review the petition and decide whether to issue a temporary order. If they believe there is an immediate risk, they can grant the order without notifying the other person (this is called an ex parte order).
3. Service of the Order
Once granted, the temporary order of protection must be served to the respondent. This means they are officially notified of the order and its restrictions.
4. Court Hearing
A hearing is scheduled, usually within a few weeks. At this hearing, both parties can present their side of the story. The judge will then decide whether to:
- Extend the order and issue a final order of protection
- Modify the terms of the order
- Dismiss the order if they find no further need for protection
5. Legal Enforcement
A temporary order of protection is legally enforceable, meaning law enforcement can arrest someone who violates its terms. Depending on the violation, the respondent may face criminal charges, fines, or jail time.
What Restrictions Can a Temporary Order of Protection Include?
A temporary order of protection may include a range of restrictions based on the severity of the situation. Some common conditions include:
- No Contact – The respondent cannot contact the petitioner in any way (calls, texts, emails, social media, or in person).
- Stay Away – The respondent must stay a certain distance away from the petitioner’s home, workplace, or children’s school.
- Firearm Surrender – In cases involving threats or violence, the court may order the respondent to surrender any firearms.
- Temporary Custody or Visitation Restrictions – If children are involved, the order may include specific conditions regarding custody and visitation.
- No Third-Party Contact – The respondent may be prohibited from asking a friend or family member to contact the petitioner on their behalf.
How Long Does a Temporary Order of Protection Last?
A temporary order of protection remains in effect until the scheduled court hearing. This could be anywhere from a few days to a few weeks, depending on the court’s availability.
If the judge determines that continued protection is necessary, they may issue a final order of protection, which can last months or even years.
What Happens If Someone Violates a Temporary Order of Protection?
Violating a temporary order of protection is a serious offense. Law enforcement has the power to arrest anyone who does not follow the order’s terms.
Consequences of Violating a Temporary Order of Protection:
- Criminal Contempt Charges – In New York, violating an order can result in criminal contempt charges (Penal Law § 215.50).
- Fines and Probation – The court may impose fines, probation, or additional restrictions on the respondent.
- Jail Time – If the violation is severe, the respondent may face misdemeanor or felony charges, leading to possible jail time.
If you believe an order has been violated, it’s important to contact law enforcement or an attorney right away.
Temporary Order of Protection vs. Regular Order of Protection
A temporary order of protection is different from a final (or regular) order of protection in a few key ways:
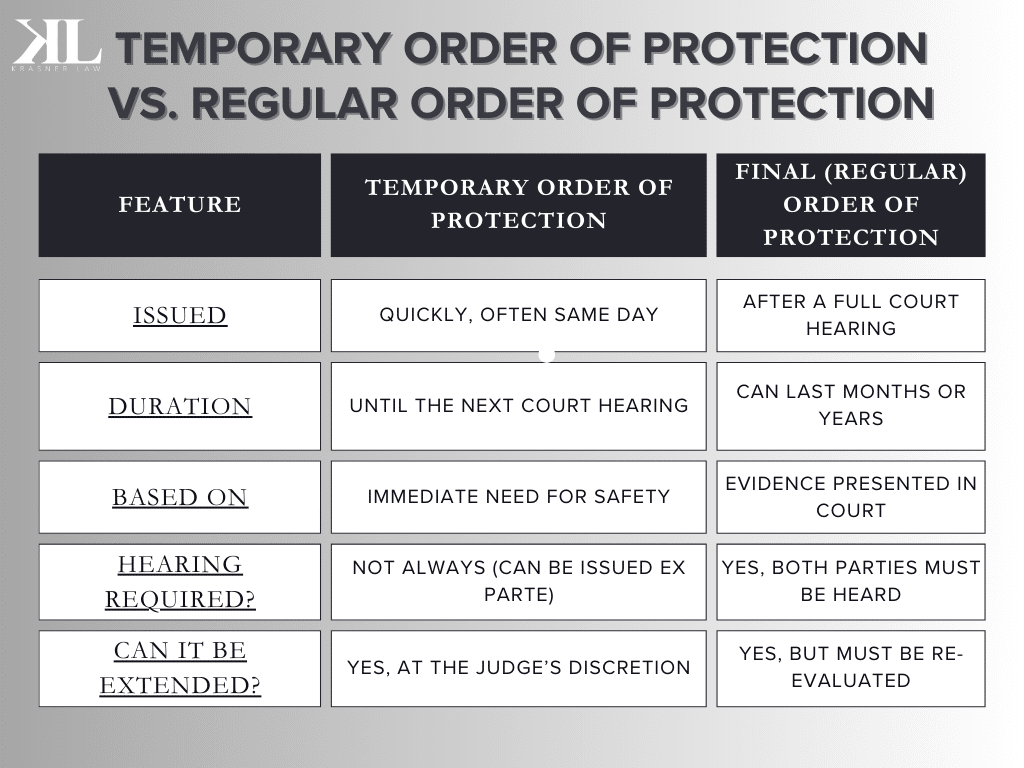
A final order of protection offers longer-term protection and typically includes stronger legal enforcement.
Relevant Laws for Temporary Orders of Protection
The rules surrounding temporary orders of protection vary by state. Here are the key laws for New York and New Jersey:
New York Laws
- Family Court Act § 828 – Allows for temporary orders of protection in family offense cases.
- Criminal Procedure Law § 530.12 – Governs orders of protection in criminal cases.
- Penal Law § 215.50 – Defines criminal contempt for violating a protection order.
New Jersey Laws
- New Jersey Prevention of Domestic Violence Act (N.J.S.A. 2C:25-17 to 2C:25-35) – Provides guidelines for protective orders.
- N.J.S.A. 2C:29-9 – Covers penalties for violating an order of protection.
If you need to file a temporary order of protection, it’s important to consult an attorney familiar with your state’s specific laws.
Need Legal Help with a Temporary Order of Protection?
If you’re dealing with a temporary order of protection, whether you need to request one or defend yourself against one, legal guidance is essential. These orders can impact your life in significant ways, and having an experienced attorney on your side can help you navigate the process.
At Krasner Law, we practice in family law and protective orders, providing compassionate and knowledgeable legal representation. If you need assistance, visit our website or contact us today for a consultation.
When Is a Temporary Order of Protection Issued?
Family Law Cases
In family court, a person can request a temporary order of protection if they are experiencing abuse, harassment, or threats from a family member, spouse, or co-parent. The order can also help protect children in dangerous situations.
Criminal Cases
If someone is arrested for domestic violence, stalking, or assault, a prosecutor may ask the court for a temporary order of protection to protect the victim.
Divorce and Custody Disputes
Sometimes, during a divorce or custody case, a temporary order of protection is needed if one parent or spouse feels unsafe. The order can set rules about contact, visitation, and other interactions.
How to Get a Temporary Order of Protection in New York and New Jersey
If you are experiencing threats, harassment, or violence, a temporary order of protection (TOP) can provide immediate legal protection. The process for obtaining one in New York and New Jersey is designed to be accessible, but it’s important to understand the steps involved and what to expect along the way.
Filing for a Temporary Order of Protection
Where Do You File for an Order?
The process for getting a temporary order of protection depends on the type of case and your relationship with the person you are seeking protection from.
- Family Court: If the situation involves a family member, spouse, former spouse, co-parent, or someone you have an intimate relationship with, you can file in Family Court.
- Criminal Court: If the person you need protection from has committed a crime against you, such as assault, harassment, or stalking, the District Attorney can request an order on your behalf in Criminal Court.
- Supreme Court: If you are going through a divorce and need protection from your spouse, you can request a temporary order of protection as part of your divorce case.
What Information Do You Need to Provide?
To file for a temporary order of protection, you will need to complete a petition that explains why you need protection. This petition should include:
- The name of the person (respondent) you are seeking protection from
- A detailed description of the incidents that led to the request, including any threats, harassment, physical violence, or stalking
- Any evidence or documentation you have, such as text messages, emails, police reports, or medical records
- Names of any witnesses who can support your claims
Once you file the petition, a court date will be set for a judge to review your case.
What Happens After You File?
1. Judge Reviews the Petition
Once your petition is submitted, a Family Court judge will review it, often the same day. If the judge believes that you are in immediate danger, they can grant a temporary order of protection right away—even before the other person (the respondent) has a chance to respond.
In Criminal Court, if the case involves an arrest, a judge will typically decide whether to issue a temporary order of protection at the respondent’s arraignment (the first court appearance after an arrest).
2. The Respondent Is Notified
Once the order is granted, it must be served to the respondent so they are officially notified of the restrictions. This is usually done by:
- A law enforcement officer
- A process server
- Another adult who is not involved in the case
The respondent is given a court date when they will have the opportunity to tell their side of the story.
3. The Court Hearing
The temporary order of protection remains in effect until the court hearing, which is typically scheduled within a few weeks. At this hearing:
- Both the petitioner and the respondent will have a chance to present their side.
- Evidence, witnesses, and testimony may be considered.
- The judge will determine whether to extend, modify, or dismiss the order.
If the judge believes ongoing protection is necessary, they will issue a final order of protection, which can last for months or even years.
What Can a Temporary Order of Protection Do?
A temporary order of protection includes legally enforceable restrictions designed to keep the petitioner safe. The judge tailors the order to the specific situation, but common restrictions include:
1. No Contact
The respondent is prohibited from contacting the petitioner in any way—this includes:
- Phone calls
- Text messages
- Emails
- Social media messages
- Communicating through a third party
Even indirect contact, such as leaving a note on a car or liking a social media post, could be considered a violation.
2. Stay Away Order
The respondent may be required to stay a certain distance from the petitioner, their home, workplace, school, or other locations they frequent. This distance is typically 100 to 500 feet, depending on the case.
3. Firearm Surrender
In cases involving threats, violence, or a history of domestic abuse, the judge may order the respondent to surrender any firearms they own to law enforcement. This is required under both New York and New Jersey laws to help prevent escalation.
4. Temporary Custody and Visitation Restrictions
If children are involved, the temporary order of protection may:
- Grant the petitioner temporary sole custody
- Set supervised visitation terms
- Prohibit the respondent from taking the child out of the state
The judge makes these decisions based on what they believe is in the best interest of the child.
What Happens If Someone Violates a Temporary Order of Protection?
Violating a temporary order of protection is a serious offense and can result in immediate legal consequences.
Consequences of Violating a Temporary Order of Protection:
- Criminal Contempt Charges – In New York, this is covered under Penal Law § 215.50, which can result in fines, probation, or jail time.
- Fines and Probation – Depending on the severity of the violation, the respondent may face financial penalties and/or supervised probation.
- Jail Time – More serious violations, such as repeated threats or physical harm, can lead to misdemeanor or felony charges, with potential prison sentences.
If the petitioner believes the order has been violated, they should immediately report it to law enforcement or their attorney.
What Happens When a Temporary Order of Protection Expires?
A temporary order of protection does not last forever. Since it is temporary, it expires when a final hearing is held in court.
If the Judge Determines Protection Is Still Needed:
The judge may issue a final order of protection, which can last months or years, depending on the situation. This order can include the same restrictions as the temporary order or be modified based on new circumstances.
If the Judge Finds No Further Need for Protection:
The temporary order of protection will end, and all restrictions will be lifted. This means the respondent can legally contact the petitioner again, unless another legal restriction applies.
If the petitioner still feels unsafe after a temporary order of protection expires, they can file a request for an extension or a new order, depending on the circumstances.
Do You Need Legal Help with a Temporary Order of Protection?
If you need a temporary order of protection, it’s important to act quickly and understand your rights. Likewise, if you are facing a TOP issued against you, knowing the legal process and following the order carefully can help you avoid further legal trouble.
At Krasner Law, we provide guidance and representation for individuals seeking or responding to orders of protection in New York and New Jersey. If you need help with the process, reach out to us today to discuss your situation.
Having a temporary order of protection in place can make a big difference in your safety and peace of mind. Whether you’re seeking protection or defending against an unfair order, legal support is key to navigating the process effectively.
Do You Need Legal Help with a Temporary Order of Protection?
Whether you need to request a temporary order of protection or are dealing with one issued against you, having the right legal guidance is important. The process can feel overwhelming, but you don’t have to go through it alone.
At Krasner Law, we understand family law and protective orders, helping individuals navigate these complex situations with confidence. If you need legal support, visit our website or contact us today.
Understanding what a temporary order of protection is and how it works can help you make informed decisions to protect yourself and your future. If you’re facing a difficult legal situation, reach out for help today.







